Perhaps you’ve recently tested your pool water and noticed that the pH and alkalinity levels were a bit high. In this article, I’ll be showing you how to lower these chemical levels using sodium bisulfate, as well as how much you’ll need, any safety concerns you should be aware of, and any alternatives to it.
If you’re in a hurry, here’s what you need to know about using sodium bisulfate in your pool:
- 10-25 ounces per 10,000 gallons of water lowers alkalinity by 10 ppm
- 5-7 ounces per 10,000 gallons of water lowers pH by approximately 0.1
Sodium bisulfate should be dissolved in a bucket of pool water and then added to the pool.
With the above, measurements, it’s important to know that the exact amount of sodium bisulfate varies quite a lot depending on the Total Alkalinity and the pH level. That’s why it’s important to check out the charts below for your exact situation.
Before we move on to the methods, let’s first take a look at what sodium bisulfate is so that the later steps make sense.

Article Contents
What is Sodium Bisulfate?
What is it Used For?
Sodium bisulfate is a dry acid and is mainly used as a pH reducer in pools and hot tubs or spas. It’s used not only to lower the pH and alkalinity in a pool but is useful for other household needs, such as being a cleaning agent, fungicide, herbicide, or anti-microbial agent.
How is it Made?
Sodium bisulfate is a type of acid that forms when sulfuric acid is combined with a sodium base such as sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide. Though it is a combination of an acid and a base, it’s nowhere near neutral and is still strongly acidic (with a pH of around 1).
Related Reading: Muriatic Acid Vs Sodium Bisulfate (Dry Acid) For Pools
Other Names for Sodium Bisulfate
Sodium bisulfate can come in many different names, so don’t be surprised if what you’re looking for doesn’t say sodium bisulfate right on the product. Here are some of the most common names you may find:
- pH down (commercial name)
- pH reducer (commercial name)
- Alkalinity reducer (commercial name)
- Bisulfate of soda
- Monosodium hydrogen sulfate
- Sodium hydrosulfite
- Sodium acid sulfate
- Dry acid
- Acid salt
- Sulfuric acid sodium salt
- Nitre cake (rarely)
- Niter cake (rarely)
- HNaO4S (its chemical formula)
What is Sodium Bisulfate Used for in Pools?
In a swimming pool, sodium bisulfate is used to lower the pH and alkalinity. It keeps the pH and alkalinity levels in your pool water stable by bringing their levels down if they go beyond their optimal ranges.
This way, not only will it allow chlorine (one of the most important chemicals to keep your pool clean and safe) to perform its task effectively, but it’ll also keep your pool free from cloudy water and prevent the corrosion of pool equipment.
Does Sodium Bisulfate Lower Alkalinity in a Pool?
Sodium bisulfate will lower the alkalinity in your pool, but it should only be added at the appropriate time (details of which we’ll go over later). When the alkalinity is lowered, the pH will follow.
Related Reading: How to Lower Alkalinity in Pool Without Affecting pH
Does Sodium Bisulfate Lower pH in a Pool?
Sodium bisulfate will lower the pH as well as the alkalinity in your pool. Again, it should only be used at the appropriate time.
How Much Sodium Bisulfate to Lower pH and Alkalinity in a Pool?
The easiest way to calculate the amount of sodium bisulfate is to use a pool chemical calculator like this one.
Let’s take a look at how much sodium bisulfate is needed to lower pH and alkalinity in a pool. We’ll assume the pool contains 10,000 gallons of water in both cases.
How Much is Needed to Lower pH in a Pool?
The amount of sodium bisulfate needed to lower the pH depends on two main factors:
- Pool Volume
- Initial pH Level
- Alkalinity level
In this example, we’ll be assuming the alkalinity and pool volume are both constant at 120 ppm and 10,000 gallons respectively. This way, we can focus only on how the addition of sodium bisulfate affects pH.
If the alkalinity was higher, much more sodium bisulfate would be needed to lower the pH. This is because alkalinity buffers the pH and tries to hold it stable.
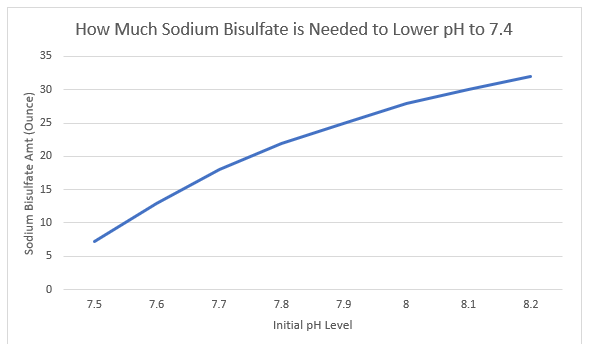
As we can see from Chart 1, there is a relatively linear positive correlation between how high the initial pH level is and the amount of sodium bisulfate needed to lower it back to normal.
Here is the above graph shown in table form:
| Initial pH Level | Sodium Bisulfate Needed (Ounces) |
| 7.5 | 7.2 |
| 7.6 | 13 |
| 7.7 | 18 |
| 7.8 | 22 |
| 7.9 | 25 |
| 8.0 | 28 |
| 8.1 | 30 |
| 8.2 | 32 |
How Much is Needed to Lower Alkalinity in a Pool?
Again, the amount of sodium bisulfate needed to lower alkalinity is dependent on:
- Pool Volume
- Initial Alkalinity Level
In this example, we’ll assume that the pH is stable and the pool volume is 10,000 gallons.
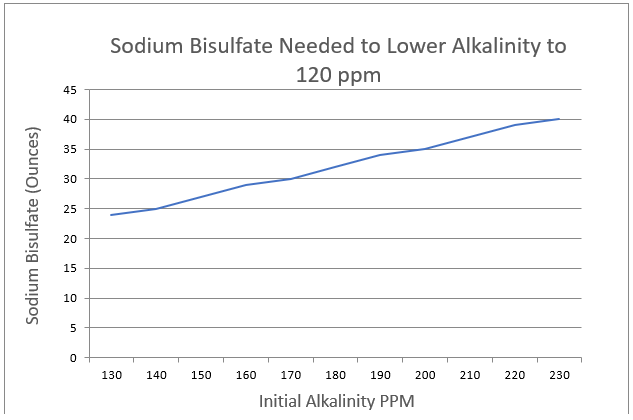
Similar to pH, there is a linear positive correlation between how high the initial alkalinity level is and how much sodium bisulfate you’ll need to lower it down to normal. The difference here is that you’ll need a much higher dose of sodium bisulfate to lower any alkalinity than you’ll need to lower the pH.
Here is the above graph shown in table form:
| Starting Alkalinity | Sodium Bisulfate (Ounces) @ pH 7.8 |
| 130 | 24 |
| 140 | 25 |
| 150 | 27 |
| 160 | 29 |
| 170 | 30 |
| 180 | 32 |
| 190 | 34 |
| 200 | 35 |
| 210 | 27 |
| 220 | 39 |
| 230 | 40 |
How to Lower pH with Sodium Bisulfate
You can follow these steps to lower your pool water’s pH level using sodium bisulfate. Keep in mind that these are general instructions and that you should always follow the instructions listed on your specific product.
1. Test the Pool Water
Before you start working with sodium bisulfate, check to see if the current pH levels in your pool water warrant any action. Your pool’s pH level should be between 7.2 and 7.6; if your pH level turns out to be higher than 7.6, it’s time to consider re-balancing the pool chemistry.

2. Figure Out How Much You’ll Need
If your specific product doesn’t have instructions, use the chart provided earlier to decide how much acid to add (remember, the chart assumes you have a 10,000-gallon pool). If your product does come with instructions, follow those carefully, but only add about three-quarters of what is recommended as it’s very important not to add too much acid. You can add the remaining later if necessary.
3. Dissolve the Acid
It’s usually best to dissolve the acid in a bucket of pool water first. It’s particularly important if you have a pool with a liner. You don’t want acid granules sitting on the bottom.
Always add water to the bucket and then the chemical, not the other way around. It can cause a dangerous reaction otherwise. Never mix sodium bisulfate with any other undiluted chemical either.
4. Add the Sodium Bisulfate to Your Pool
Once the preparations are done, pour the acid into your pool near the jets and not the intake/skimmer (for inground pools) and around the pool walls (for above-ground pools). This allows the acid to dissolve and spread more evenly within the pool water.
As sodium bisulfate is an acid, it’s important that you avoid handling it on a windy day as the granules or powder can be blown onto and cause damage to your skin or clothing.
5. Wait for a Few Hours
There’s not much to do now but wait for the sodium bisulfate to do its job. Wait approximately 6 hours before retesting your pool water.
6. Retest the pH of the Water
After 6 hours have passed, it’s time to retest the chemistry of your pool water. If the pH is down to within its optimal range, you’re good to go. Otherwise, you can repeat the previous steps until the pH level is where it should be.
Related Reading: How to Lower Alkalinity | Pool Alkalinity High
How to Lower Alkalinity with Sodium Bisulfate
Now, let’s take a look at how you can lower the alkalinity in your pool using sodium bisulfate. Again, these instructions are general and you should always follow the instructions specifically listed on your product.
1. Test the Pool Water
Again, make sure to test your pool water first to make sure alkalinity levels are above their optimal range (typically between 100 and 150 ppm). If it’s higher than 150 ppm, you can add sodium bisulfate to lower it. The pH will reduce at the same time.

2. Figure Out How Much You’ll Need
Like before, if your product has instructions on how much to use for your particular alkalinity level and pool size, make sure to follow those carefully. Otherwise, use the chart provided earlier to get a rough estimate of how much sodium bisulfate you’ll need (keep in mind that the chart is mostly relevant for a 10,000-gallon pool).
Like with adjusting your pH, add only about ¾ of the recommended amount; you can add the rest later if necessary.
3. Dilute the Sodium Bisulfate
Fill up a large bucket about ¾ of the way with water and add the sodium bisulfate to it. Use a wooden stick or stirrer to mix the solution well until all the acid is dissolved.
4. Turn Off Your Jets
Unlike what you’d do to lower the pH, here you’ll have to turn the jets off instead of using them to distribute the acid.

5. Slowly Pour the Acid In
Slowly and carefully pour the dissolved acid into the water around the pool’s perimeter and starting near the deep end.
6. Wait a Few Hours
Like before, you’ll have to wait about 6 hours for the sodium bisulfate to do its job before you retest the water chemistry.
7. Retest and Repeat the Whole Process if Necessary
Finally, it’s time to retest the pool water chemistry to make sure the alkalinity levels are where they should be. If they’re still too high, add the remainder of the acid until they drop to their optimal range.
pH is Too Low but Alkalinity is Correct
When you lower the alkalinity, the pH will follow. Sometimes it will go below the recommended level of 7.4-7.6. What should you do in this case?
If the pH is around 7.1-7.3, you can aerate the water. Just turn on the jets and point them up. Turn on any water features you have too and leave the pool overnight.
The aeration will naturally increase the pH level.
If the pH is below 7.1, you can add a small amount of soda ash or baking soda. Be careful not to overdo it.
Does Sodium Bisulfate Lower Pool Chlorine?
Adding sodium bisulfate to your pool water doesn’t lower the pool chlorine concentration in the water. If the pH and alkalinity are not too high, sodium bisulfate will lower the pH which enhances the effectiveness of chlorine.
Is Sodium Bisulfate Safe?
Sodium bisulfate is a safe chemical to use for your pool, though you should still use protective equipment, such as a mask and gloves since it is an acid. Compared with muriatic acid though, sodium bisulfate is much safer to handle as there’s no risk of spilling or splashing the chemical.
Though it’s considered safe for humans by the FDA, sodium bisulfate should not be handled carelessly. You should always wait at least 6 hours after adding the acid to the pool before entering the water. You’ll also need to be careful not to add too much to the water since it result in a high concentration of sulfates and damage the pool surface and plumbing.
Is Sodium Bisulfate Natural?
Sodium bisulfate is considered natural since it’s made with minerals, however, commercially available sodium bisulfate is produced using sulfur-extracted sulfuric acid through a chemical process.
Alternatives to Sodium Bisulfate
There are two main alternatives to using sodium bisulfate in your pool:
- Muriatic Acid or Hydrochloric Acid
- Sulfuric Acid
Muriatic acid (less concentrated Hydrochloric Acid) is usually the number one alternative to sodium bisulfate. They both do the same job of lowering the pH and alkalinity of your pool but have some differences.
Muriatic acid is more dangerous to handle, works quicker, is cheaper, and doesn’t leave behind residue.
Sulfuric acid is another alternative in that it’ll also do the same job as sodium bisulfate. However, its strength is similar to that of muriatic acid. What differentiates sulfuric acid from muriatic acid is the fact that the former leaves behind sulfates while the latter leaves chlorides.
Vinegar may also work, but it’s very diluted. Thus, you’ll need a lot of it in your pool and at that point, it can produce a very strong odor that is probably not very pleasant for pool users. It’s not recommended.
Final Thoughts
Sodium bisulfate is a relatively easy chemical to use to lower the pH and alkalinity of your pool. As long as you keep track of how much you’re using and the water chemistry, you should be able to return to your pool in no time.

